As a physician, I frequently encounter patients who struggle with respiratory challenges, whether due to chronic conditions, temporary illnesses, or age-related health issues. For many of these individuals, maintaining adequate oxygen levels is critical to their well-being, recovery, and quality of life. While supplemental oxygen has traditionally been administered in clinical settings or through cumbersome oxygen tanks, advances in technology have made home oxygen concentrators a practical and effective solution for a wide range of patients.
This article explores the importance of oxygen concentrators from a medical perspective, how they work, who can benefit from them, and the considerations I recommend when selecting one.
---
#### **Understanding Oxygen Concentrators**
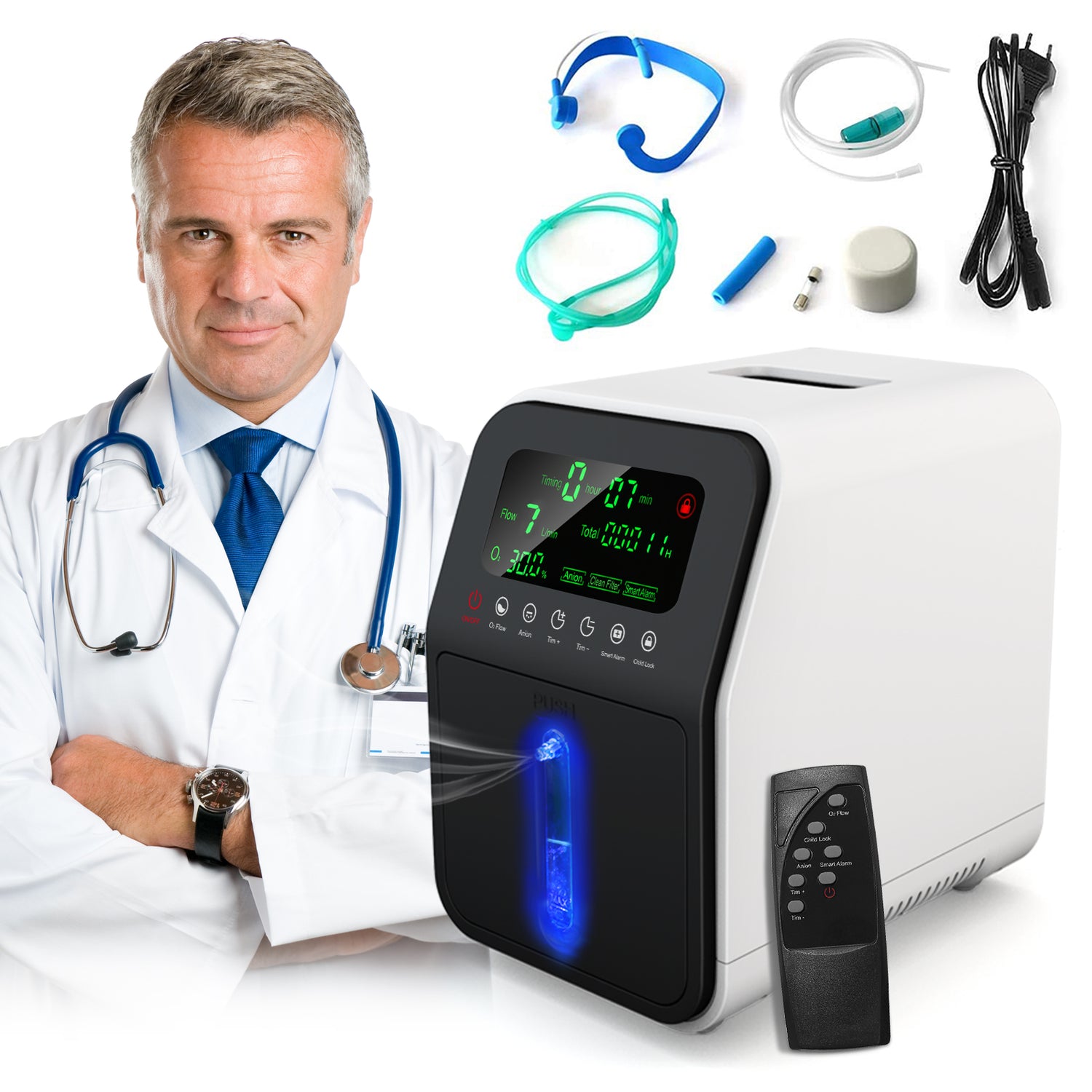
Oxygen concentrators are medical devices designed to deliver concentrated oxygen to individuals who have difficulty maintaining adequate blood oxygen levels. Unlike traditional oxygen tanks, which store pre-filled oxygen, concentrators extract oxygen from ambient air by filtering out nitrogen and other gases. This means they provide a continuous supply of oxygen, as long as they are powered.
For many patients, oxygen concentrators offer the freedom to manage their respiratory needs at home, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits or dependence on bulky equipment.
---
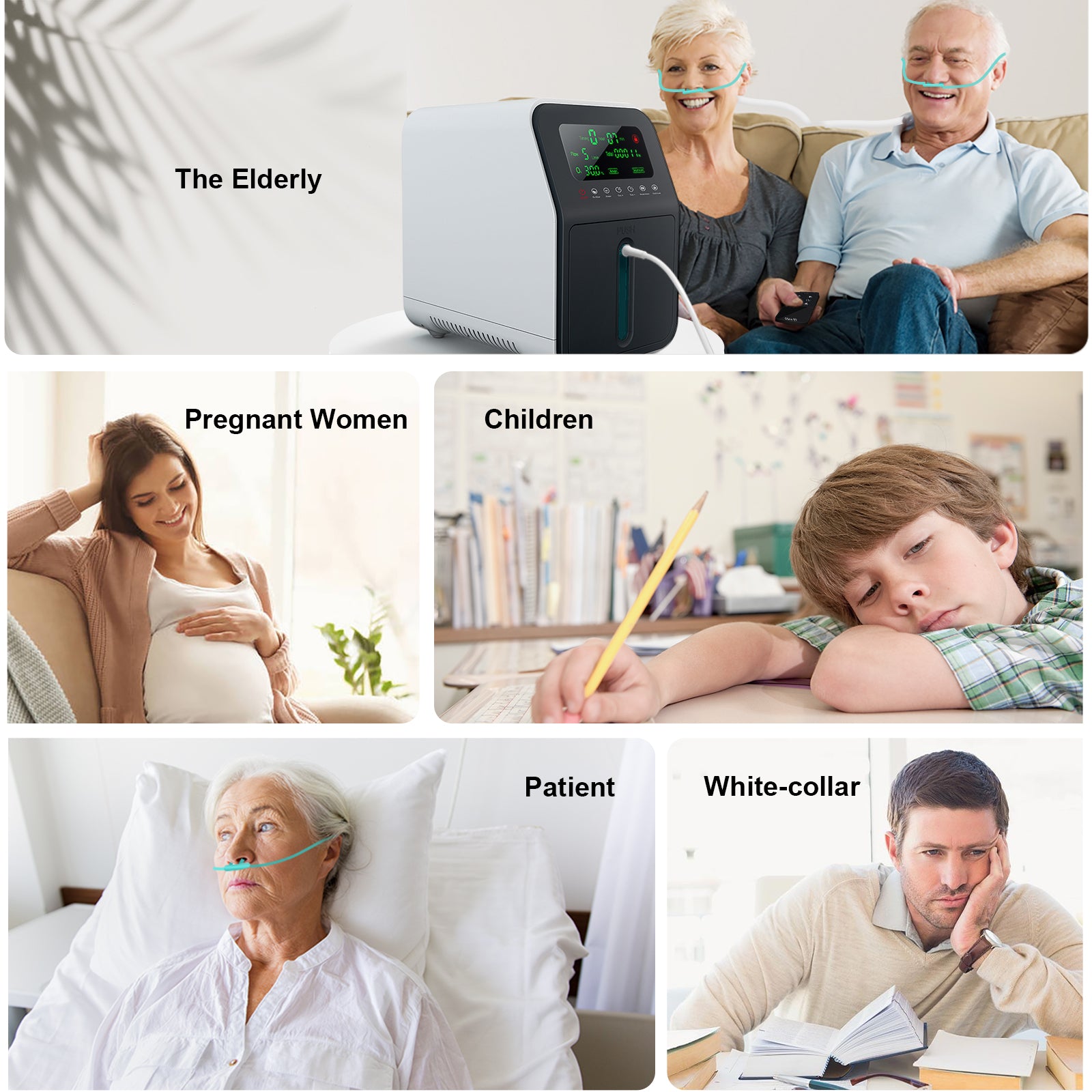
#### **Who Needs an Oxygen Concentrator?**
As a doctor, I typically recommend oxygen concentrators for patients with the following conditions or situations:
1. **Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)**
COPD is one of the most common reasons patients require supplemental oxygen. By improving oxygen levels, concentrators help reduce breathlessness and fatigue, allowing patients to carry out daily activities with greater ease.
2. **Emphysema or Chronic Bronchitis**
Patients with these forms of COPD benefit from long-term oxygen therapy to improve their overall quality of life and reduce complications.
3. **Pneumonia or Severe Respiratory Infections**
For individuals recovering from pneumonia, COVID-19, or other infections that compromise lung function, temporary use of a concentrator can accelerate recovery and prevent complications.
4. **Sleep Apnea (In Specific Cases)**
While CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) machines are the standard treatment for sleep apnea, patients with severe cases that affect oxygen saturation may benefit from supplemental oxygen at night.
5. **Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)**
For some patients with CHF, oxygen therapy can help relieve symptoms, particularly during sleep or physical exertion.
6. **Palliative Care**
Patients with advanced illnesses such as cancer or late-stage lung disease may use oxygen concentrators to improve comfort and reduce distress caused by shortness of breath.
7. **Altitude-Related Needs**
Some individuals living at or traveling to high altitudes may require oxygen concentrators to adapt to the thinner air and prevent hypoxia.
---
#### **Medical Benefits of Oxygen Concentrators**
1. **Enhanced Oxygenation**
Oxygen concentrators provide consistent oxygen delivery, helping patients maintain adequate oxygen levels in their blood. This is essential for reducing symptoms like breathlessness, fatigue, and confusion.
2. **Improved Quality of Life**
By alleviating respiratory distress, oxygen concentrators enable patients to engage in daily activities, improve sleep quality, and enjoy a greater sense of independence.
3. **Reduced Hospitalization Rates**
For many chronic respiratory conditions, access to home oxygen therapy reduces the frequency of hospital visits, allowing patients to manage their health more effectively.
4. **Support During Recovery**
Patients recovering from respiratory infections or surgeries often experience faster recovery times with supplemental oxygen, as it aids in tissue healing and energy restoration.
---
#### **Considerations When Recommending an Oxygen Concentrator**
When I advise patients or their families on purchasing an oxygen concentrator, I emphasize the following factors:
1. **Flow Rate and Oxygen Concentration**
It’s critical to choose a model that meets the patient’s prescribed oxygen flow rate, measured in liters per minute (LPM). Most home oxygen concentrators provide 1–5 LPM, while some high-capacity models can deliver up to 10 LPM.
2. **Portability**
For active patients, portable oxygen concentrators are a better option than stationary models. They are lightweight and battery-powered, allowing for mobility and ease of travel.
3. **Noise Levels**
A quiet device can significantly improve the patient’s experience, particularly for those who use it during sleep or in shared living spaces.
4. **Ease of Maintenance**
Filters should be easy to clean or replace, and the device should come with clear instructions for upkeep to ensure long-term performance.
5. **Energy Efficiency**
Since oxygen concentrators often run for hours at a time, selecting an energy-efficient model helps reduce electricity costs while ensuring reliable performance.
6. **Safety Features**
Look for models with alarms for low oxygen output, power failure, or technical malfunctions. These safety features provide reassurance to both patients and caregivers.
---
#### **Advice for Patients and Caregivers**
1. **Consult a Healthcare Provider**
Patients should never self-prescribe oxygen therapy. Always consult a doctor to determine if an oxygen concentrator is appropriate and to receive guidance on the proper flow rate and usage duration.
2. **Use as Directed**
Overusing oxygen can lead to complications such as oxygen toxicity, while underuse can fail to address the patient’s needs. Following medical instructions is crucial.
3. **Monitor Symptoms**
Patients and caregivers should monitor for changes in symptoms and report concerns such as persistent breathlessness or dizziness to their healthcare provider.
4. **Prepare for Power Outages**
Since oxygen concentrators require electricity, patients should have a backup plan, such as portable oxygen tanks, in case of power outages.
---
#### **Conclusion: A Lifesaving Tool for Respiratory Health**
As a doctor, I’ve seen firsthand the transformative impact oxygen concentrators can have on patients’ lives. These devices offer a lifeline for individuals with chronic conditions, support during recovery, and peace of mind for families.
If you or a loved one has been prescribed oxygen therapy, investing in a high-quality oxygen concentrator is an investment in health, independence, and quality of life. With proper guidance from your healthcare provider and careful selection of the right device, you can breathe easier knowing you’ve taken a vital step toward better respiratory health.
Remember, oxygen is life, and having access to it when needed can make all the difference.
This article explores the importance of oxygen concentrators from a medical perspective, how they work, who can benefit from them, and the considerations I recommend when selecting one.
---
#### **Understanding Oxygen Concentrators**
Oxygen concentrators are medical devices designed to deliver concentrated oxygen to individuals who have difficulty maintaining adequate blood oxygen levels. Unlike traditional oxygen tanks, which store pre-filled oxygen, concentrators extract oxygen from ambient air by filtering out nitrogen and other gases. This means they provide a continuous supply of oxygen, as long as they are powered.
For many patients, oxygen concentrators offer the freedom to manage their respiratory needs at home, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits or dependence on bulky equipment.
---
#### **Who Needs an Oxygen Concentrator?**
As a doctor, I typically recommend oxygen concentrators for patients with the following conditions or situations:
1. **Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)**
COPD is one of the most common reasons patients require supplemental oxygen. By improving oxygen levels, concentrators help reduce breathlessness and fatigue, allowing patients to carry out daily activities with greater ease.
2. **Emphysema or Chronic Bronchitis**
Patients with these forms of COPD benefit from long-term oxygen therapy to improve their overall quality of life and reduce complications.
3. **Pneumonia or Severe Respiratory Infections**
For individuals recovering from pneumonia, COVID-19, or other infections that compromise lung function, temporary use of a concentrator can accelerate recovery and prevent complications.
4. **Sleep Apnea (In Specific Cases)**
While CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) machines are the standard treatment for sleep apnea, patients with severe cases that affect oxygen saturation may benefit from supplemental oxygen at night.
5. **Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)**
For some patients with CHF, oxygen therapy can help relieve symptoms, particularly during sleep or physical exertion.
6. **Palliative Care**
Patients with advanced illnesses such as cancer or late-stage lung disease may use oxygen concentrators to improve comfort and reduce distress caused by shortness of breath.
7. **Altitude-Related Needs**
Some individuals living at or traveling to high altitudes may require oxygen concentrators to adapt to the thinner air and prevent hypoxia.
---
#### **Medical Benefits of Oxygen Concentrators**
1. **Enhanced Oxygenation**
Oxygen concentrators provide consistent oxygen delivery, helping patients maintain adequate oxygen levels in their blood. This is essential for reducing symptoms like breathlessness, fatigue, and confusion.
2. **Improved Quality of Life**
By alleviating respiratory distress, oxygen concentrators enable patients to engage in daily activities, improve sleep quality, and enjoy a greater sense of independence.
3. **Reduced Hospitalization Rates**
For many chronic respiratory conditions, access to home oxygen therapy reduces the frequency of hospital visits, allowing patients to manage their health more effectively.
4. **Support During Recovery**
Patients recovering from respiratory infections or surgeries often experience faster recovery times with supplemental oxygen, as it aids in tissue healing and energy restoration.
---
#### **Considerations When Recommending an Oxygen Concentrator**
When I advise patients or their families on purchasing an oxygen concentrator, I emphasize the following factors:
1. **Flow Rate and Oxygen Concentration**
It’s critical to choose a model that meets the patient’s prescribed oxygen flow rate, measured in liters per minute (LPM). Most home oxygen concentrators provide 1–5 LPM, while some high-capacity models can deliver up to 10 LPM.
2. **Portability**
For active patients, portable oxygen concentrators are a better option than stationary models. They are lightweight and battery-powered, allowing for mobility and ease of travel.
3. **Noise Levels**
A quiet device can significantly improve the patient’s experience, particularly for those who use it during sleep or in shared living spaces.
4. **Ease of Maintenance**
Filters should be easy to clean or replace, and the device should come with clear instructions for upkeep to ensure long-term performance.
5. **Energy Efficiency**
Since oxygen concentrators often run for hours at a time, selecting an energy-efficient model helps reduce electricity costs while ensuring reliable performance.
6. **Safety Features**
Look for models with alarms for low oxygen output, power failure, or technical malfunctions. These safety features provide reassurance to both patients and caregivers.
---
#### **Advice for Patients and Caregivers**
1. **Consult a Healthcare Provider**
Patients should never self-prescribe oxygen therapy. Always consult a doctor to determine if an oxygen concentrator is appropriate and to receive guidance on the proper flow rate and usage duration.
2. **Use as Directed**
Overusing oxygen can lead to complications such as oxygen toxicity, while underuse can fail to address the patient’s needs. Following medical instructions is crucial.
3. **Monitor Symptoms**
Patients and caregivers should monitor for changes in symptoms and report concerns such as persistent breathlessness or dizziness to their healthcare provider.
4. **Prepare for Power Outages**
Since oxygen concentrators require electricity, patients should have a backup plan, such as portable oxygen tanks, in case of power outages.
---
#### **Conclusion: A Lifesaving Tool for Respiratory Health**
As a doctor, I’ve seen firsthand the transformative impact oxygen concentrators can have on patients’ lives. These devices offer a lifeline for individuals with chronic conditions, support during recovery, and peace of mind for families.
If you or a loved one has been prescribed oxygen therapy, investing in a high-quality oxygen concentrator is an investment in health, independence, and quality of life. With proper guidance from your healthcare provider and careful selection of the right device, you can breathe easier knowing you’ve taken a vital step toward better respiratory health.
Remember, oxygen is life, and having access to it when needed can make all the difference.


1 comment
Weihong Ran
Where is the fuse located?
Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.