Oxygen concentrators have become a vital piece of medical equipment for individuals suffering from respiratory issues. As a non-invasive therapy, these devices help people with conditions like COPD, asthma, and other lung diseases maintain better oxygen levels. However, like any medical technology, oxygen concentrators come with both benefits and limitations.
This guide will explore the advantages and disadvantages of oxygen concentrators in-depth, covering essential factors to consider before making a purchase. We will also look at some real-life examples, offer practical advice, and touch on the latest innovations in the field.
---
### **Part 1: Understanding Oxygen Concentrators**
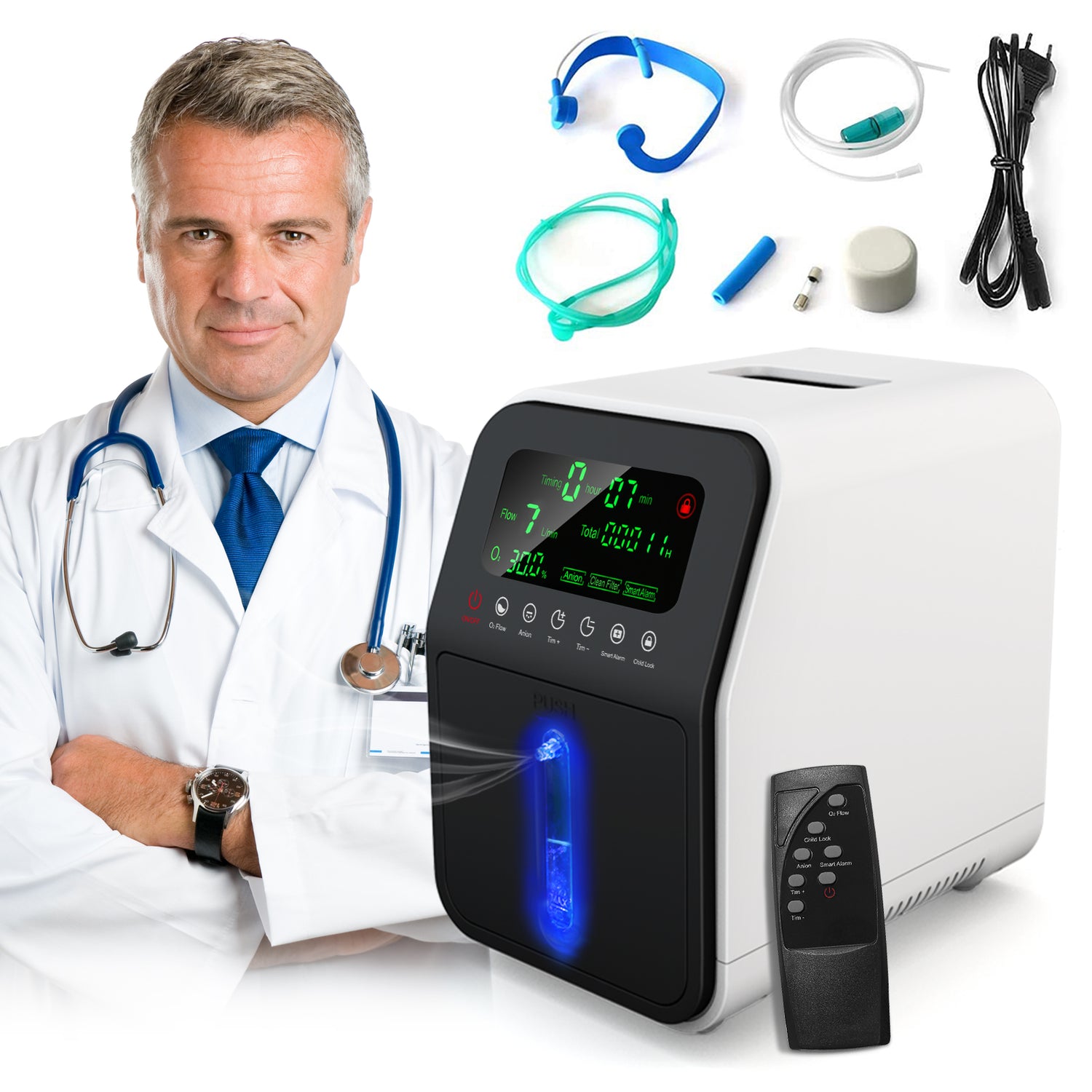
Oxygen concentrators are medical devices that deliver oxygen to patients who have difficulty maintaining healthy blood oxygen levels. These devices extract oxygen from ambient air, filter it, and provide a more concentrated flow to the user. Unlike traditional oxygen tanks, concentrators do not require refills; they continually generate oxygen as long as they are powered.
#### Types of Oxygen Concentrators
1. **Stationary Oxygen Concentrators**: These are larger units designed for home use, offering continuous flow and higher oxygen output. They typically require a direct electrical connection.
2. **Portable Oxygen Concentrators (POCs)**: These smaller, battery-powered units allow users to move freely while receiving oxygen therapy. They are ideal for people who lead an active lifestyle and need mobility.
---
### **Part 2: Top 10 Pros of Oxygen Concentrators**
1. **No Refills Needed**
Unlike oxygen tanks that need to be regularly refilled, oxygen concentrators draw oxygen from the surrounding air. This reduces the dependency on external suppliers, providing a continuous oxygen source as long as the device is powered【18†source】.
2. **Improved Mobility and Quality of Life**
Portable oxygen concentrators allow users to maintain an active lifestyle, as they can carry the device with them wherever they go. Many modern units are lightweight and come with features like carrying cases and backpacks for added convenience【19†source】.
3. **Cost-Effective in the Long Run**
While the upfront cost of an oxygen concentrator can be high, it eliminates the recurring expenses associated with oxygen tank refills. Over time, this makes concentrators a more economical option for patients who require long-term oxygen therapy【18†source】【19†source】.
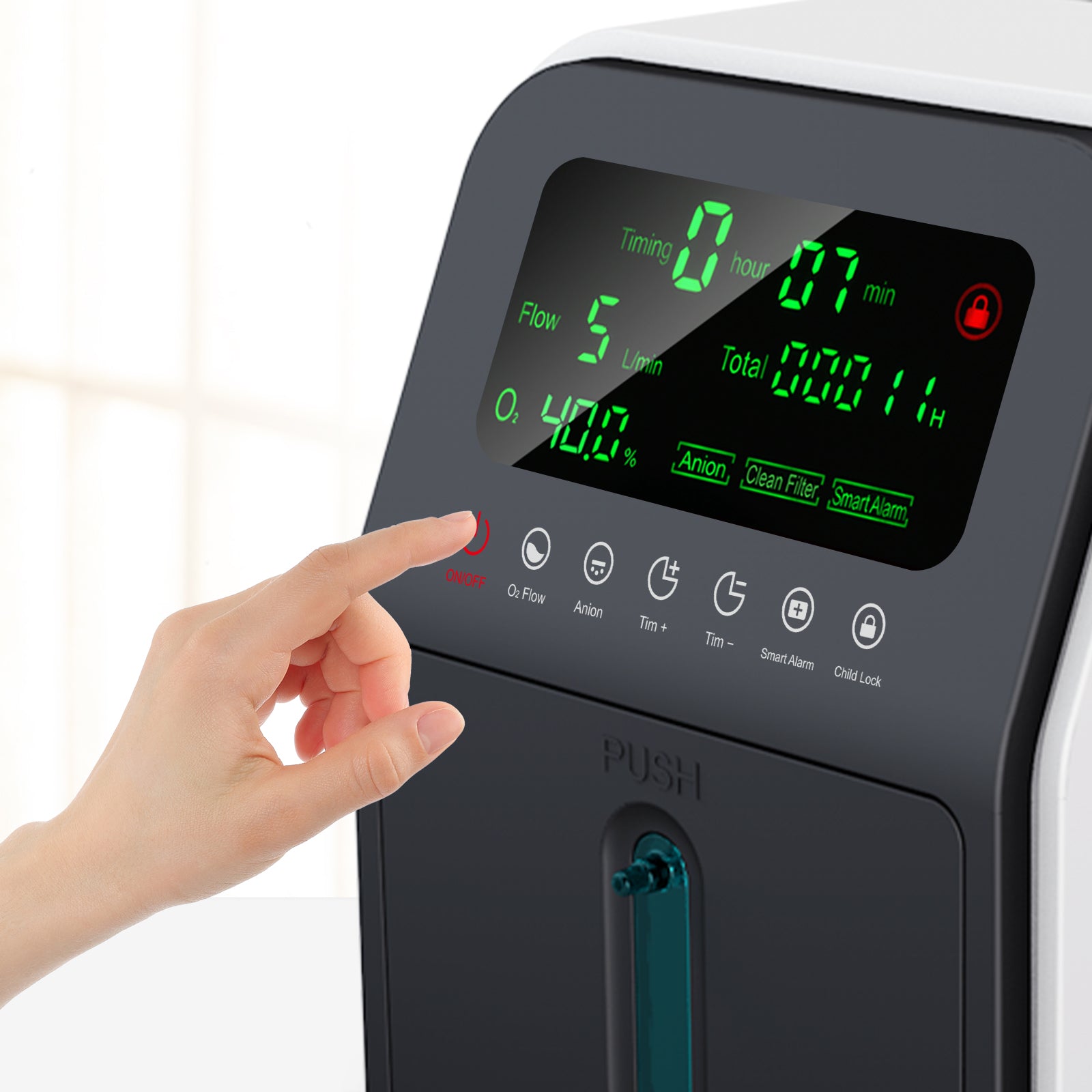
4. **Customizable Oxygen Flow**
Many concentrators offer both continuous and pulse-dose modes, allowing users to customize oxygen delivery based on their activity level. Continuous flow is ideal for stationary use, while pulse-dose mode is more efficient for active users【19†source】.
5. **Portability Options**
Devices like the Philips Respironics SimplyGo POC are designed with portability in mind. Weighing just 10 pounds, this model is light enough for travel, making it suitable for users who need oxygen therapy on the go【19†source】.
6. **Reduced Symptom Severity**
For individuals with conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pulmonary fibrosis, or severe asthma, oxygen therapy can help alleviate symptoms by improving oxygen saturation levels in the blood. This leads to better overall health, improved energy, and enhanced physical performance【18†source】.
7. **Extended Battery Life**
Modern portable concentrators often come with long-lasting, rechargeable batteries that can sustain several hours of use. Devices like the O2 Concepts OxLife Independence Portable Oxygen Concentrator are equipped with additional power options, such as external battery chargers, making them perfect for long trips【19†source】.
8. **FAA Approval for Air Travel**
Many portable oxygen concentrators are approved by the FAA for use on commercial airlines. This means that users can maintain their oxygen therapy while flying, enabling them to travel for work or leisure without compromising their health【19†source】.
9. **Energy Efficiency**
Today’s oxygen concentrators are designed with energy-saving features, making them more efficient and less expensive to operate. Some models consume minimal power while still providing a consistent oxygen output【18†source】.
10. **Improved Sleep Quality**
Oxygen concentrators can help people with conditions like sleep apnea or heart failure, where supplemental oxygen improves breathing during sleep. Many models include sleep modes that ensure a continuous oxygen flow throughout the night【19†source】.
---
### **Part 3: Top 10 Cons of Oxygen Concentrators**
1. **Initial Cost**
While oxygen concentrators save money in the long term, the upfront cost can be prohibitively expensive for some users. High-end models can cost upwards of $2,000 or more, though insurance or government programs may help cover these expenses【18†source】【19†source】.
2. **Power Dependency**
Oxygen concentrators require a consistent power source to operate. In the event of a power outage, patients may need a backup oxygen supply. Portable models help address this issue by offering rechargeable batteries, but battery life is limited【18†source】.
3. **Noise Levels**
Although many newer concentrators are designed to operate quietly, some models still generate ambient noise, especially during nighttime use. This can be disruptive for patients and their families, particularly in quiet settings【18†source】.
4. **Size and Weight**
While portable models have come a long way in terms of size and weight, some concentrators are still too bulky or heavy for certain users, particularly those with limited mobility or strength【19†source】.
5. **Limited Oxygen Concentration**
Most oxygen concentrators provide oxygen at a concentration level of 90-95%. For patients requiring 100% pure oxygen, these devices may not be suitable, and traditional oxygen tanks might be necessary【18†source】.
6. **Restricted High-Flow Options**
While some concentrators can deliver high flow rates, they are generally not as efficient as traditional oxygen tanks at delivering oxygen to patients with severe respiratory issues. Patients needing a high flow rate might find concentrators inadequate【18†source】.
7. **Battery Life for Portable Models**
Even with improved battery technology, portable oxygen concentrators typically offer only a few hours of operation before needing to be recharged. This limits their use for long-distance travel or extended outdoor activities【19†source】.
8. **Heat Generation**
Concentrators, especially when used for extended periods, can generate heat. This might be uncomfortable for patients, especially in warm climates or during summer months【18†source】.
9. **Maintenance Requirements**
Oxygen concentrators require regular maintenance, including filter changes and cleaning, to ensure optimal performance. Failure to maintain the device properly can lead to decreased oxygen output and potential health risks【18†source】.
10. **Possible Supply Disruptions**
Any malfunction in the device, such as a power failure or mechanical issue, can disrupt oxygen supply, which can be dangerous for patients relying on a constant oxygen flow. Backup systems are often necessary to mitigate these risks【18†source】.
---
### **Part 4: How to Choose the Right Oxygen Concentrator**
#### 1. **Assessing Your Needs**
The first step in choosing an oxygen concentrator is understanding your medical needs. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the required oxygen flow rate, whether you need continuous or pulse-dose delivery, and how often you'll need oxygen therapy. Patients with severe respiratory issues may need a higher flow rate than those with milder conditions.
#### 2. **Portability vs. Stationary Use**
If you lead an active lifestyle, a portable oxygen concentrator may be the best option. However, if you spend most of your time at home, a stationary model might offer better performance and value for money. Stationary models usually provide higher oxygen flow rates but are bulkier.
#### 3. **Battery Life and Power Options**
If you opt for a portable concentrator, consider its battery life. Some models offer extended battery options or external chargers, which are essential for long trips. You should also look for devices with both AC and DC power supplies, so you can use them at home or in the car【19†source】.
#### 4. **Noise Levels**
Noise can be an important factor, especially if you plan to use the concentrator at night or in quiet environments. Be sure to choose a model known for its quiet operation to avoid disruptions during sleep or other quiet activities.
#### 5. **Weight and Size**
For those who need a portable model, weight and size are critical factors. Look for lightweight models with ergonomic designs and features like rolling carts or backpacks for easy transport【19†source】.
#### 6. **FAA Approval and Travel-Friendly Features**
If you travel frequently, especially by air, be sure to select an FAA-approved portable oxygen concentrator. Features like compact size and easy battery swapping can make travel much more convenient【19†source】.
#### 7. **Cost and Insurance Coverage**
The cost of an oxygen concentrator can vary widely depending on the features, brand, and type of device. Check if your insurance covers part of the cost, or explore government assistance programs designed to help cover the expense.
---
### **Conclusion**
Oxygen concentrators have transformed the lives of many individuals suffering from chronic respiratory conditions. While they offer numerous benefits such as improved mobility, reduced costs, and customizable oxygen delivery, they also come with limitations, including initial cost, noise, and power dependency. By understanding the pros and cons of these devices and selecting the right model based on your specific
This guide will explore the advantages and disadvantages of oxygen concentrators in-depth, covering essential factors to consider before making a purchase. We will also look at some real-life examples, offer practical advice, and touch on the latest innovations in the field.
---
### **Part 1: Understanding Oxygen Concentrators**
Oxygen concentrators are medical devices that deliver oxygen to patients who have difficulty maintaining healthy blood oxygen levels. These devices extract oxygen from ambient air, filter it, and provide a more concentrated flow to the user. Unlike traditional oxygen tanks, concentrators do not require refills; they continually generate oxygen as long as they are powered.
#### Types of Oxygen Concentrators
1. **Stationary Oxygen Concentrators**: These are larger units designed for home use, offering continuous flow and higher oxygen output. They typically require a direct electrical connection.
2. **Portable Oxygen Concentrators (POCs)**: These smaller, battery-powered units allow users to move freely while receiving oxygen therapy. They are ideal for people who lead an active lifestyle and need mobility.
---
### **Part 2: Top 10 Pros of Oxygen Concentrators**
1. **No Refills Needed**
Unlike oxygen tanks that need to be regularly refilled, oxygen concentrators draw oxygen from the surrounding air. This reduces the dependency on external suppliers, providing a continuous oxygen source as long as the device is powered【18†source】.
2. **Improved Mobility and Quality of Life**
Portable oxygen concentrators allow users to maintain an active lifestyle, as they can carry the device with them wherever they go. Many modern units are lightweight and come with features like carrying cases and backpacks for added convenience【19†source】.
3. **Cost-Effective in the Long Run**
While the upfront cost of an oxygen concentrator can be high, it eliminates the recurring expenses associated with oxygen tank refills. Over time, this makes concentrators a more economical option for patients who require long-term oxygen therapy【18†source】【19†source】.
4. **Customizable Oxygen Flow**
Many concentrators offer both continuous and pulse-dose modes, allowing users to customize oxygen delivery based on their activity level. Continuous flow is ideal for stationary use, while pulse-dose mode is more efficient for active users【19†source】.
5. **Portability Options**
Devices like the Philips Respironics SimplyGo POC are designed with portability in mind. Weighing just 10 pounds, this model is light enough for travel, making it suitable for users who need oxygen therapy on the go【19†source】.
6. **Reduced Symptom Severity**
For individuals with conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pulmonary fibrosis, or severe asthma, oxygen therapy can help alleviate symptoms by improving oxygen saturation levels in the blood. This leads to better overall health, improved energy, and enhanced physical performance【18†source】.
7. **Extended Battery Life**
Modern portable concentrators often come with long-lasting, rechargeable batteries that can sustain several hours of use. Devices like the O2 Concepts OxLife Independence Portable Oxygen Concentrator are equipped with additional power options, such as external battery chargers, making them perfect for long trips【19†source】.
8. **FAA Approval for Air Travel**
Many portable oxygen concentrators are approved by the FAA for use on commercial airlines. This means that users can maintain their oxygen therapy while flying, enabling them to travel for work or leisure without compromising their health【19†source】.
9. **Energy Efficiency**
Today’s oxygen concentrators are designed with energy-saving features, making them more efficient and less expensive to operate. Some models consume minimal power while still providing a consistent oxygen output【18†source】.
10. **Improved Sleep Quality**
Oxygen concentrators can help people with conditions like sleep apnea or heart failure, where supplemental oxygen improves breathing during sleep. Many models include sleep modes that ensure a continuous oxygen flow throughout the night【19†source】.
---
### **Part 3: Top 10 Cons of Oxygen Concentrators**
1. **Initial Cost**
While oxygen concentrators save money in the long term, the upfront cost can be prohibitively expensive for some users. High-end models can cost upwards of $2,000 or more, though insurance or government programs may help cover these expenses【18†source】【19†source】.
2. **Power Dependency**
Oxygen concentrators require a consistent power source to operate. In the event of a power outage, patients may need a backup oxygen supply. Portable models help address this issue by offering rechargeable batteries, but battery life is limited【18†source】.
3. **Noise Levels**
Although many newer concentrators are designed to operate quietly, some models still generate ambient noise, especially during nighttime use. This can be disruptive for patients and their families, particularly in quiet settings【18†source】.
4. **Size and Weight**
While portable models have come a long way in terms of size and weight, some concentrators are still too bulky or heavy for certain users, particularly those with limited mobility or strength【19†source】.
5. **Limited Oxygen Concentration**
Most oxygen concentrators provide oxygen at a concentration level of 90-95%. For patients requiring 100% pure oxygen, these devices may not be suitable, and traditional oxygen tanks might be necessary【18†source】.
6. **Restricted High-Flow Options**
While some concentrators can deliver high flow rates, they are generally not as efficient as traditional oxygen tanks at delivering oxygen to patients with severe respiratory issues. Patients needing a high flow rate might find concentrators inadequate【18†source】.
7. **Battery Life for Portable Models**
Even with improved battery technology, portable oxygen concentrators typically offer only a few hours of operation before needing to be recharged. This limits their use for long-distance travel or extended outdoor activities【19†source】.
8. **Heat Generation**
Concentrators, especially when used for extended periods, can generate heat. This might be uncomfortable for patients, especially in warm climates or during summer months【18†source】.
9. **Maintenance Requirements**
Oxygen concentrators require regular maintenance, including filter changes and cleaning, to ensure optimal performance. Failure to maintain the device properly can lead to decreased oxygen output and potential health risks【18†source】.
10. **Possible Supply Disruptions**
Any malfunction in the device, such as a power failure or mechanical issue, can disrupt oxygen supply, which can be dangerous for patients relying on a constant oxygen flow. Backup systems are often necessary to mitigate these risks【18†source】.
---
### **Part 4: How to Choose the Right Oxygen Concentrator**
#### 1. **Assessing Your Needs**
The first step in choosing an oxygen concentrator is understanding your medical needs. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the required oxygen flow rate, whether you need continuous or pulse-dose delivery, and how often you'll need oxygen therapy. Patients with severe respiratory issues may need a higher flow rate than those with milder conditions.
#### 2. **Portability vs. Stationary Use**
If you lead an active lifestyle, a portable oxygen concentrator may be the best option. However, if you spend most of your time at home, a stationary model might offer better performance and value for money. Stationary models usually provide higher oxygen flow rates but are bulkier.
#### 3. **Battery Life and Power Options**
If you opt for a portable concentrator, consider its battery life. Some models offer extended battery options or external chargers, which are essential for long trips. You should also look for devices with both AC and DC power supplies, so you can use them at home or in the car【19†source】.
#### 4. **Noise Levels**
Noise can be an important factor, especially if you plan to use the concentrator at night or in quiet environments. Be sure to choose a model known for its quiet operation to avoid disruptions during sleep or other quiet activities.
#### 5. **Weight and Size**
For those who need a portable model, weight and size are critical factors. Look for lightweight models with ergonomic designs and features like rolling carts or backpacks for easy transport【19†source】.
#### 6. **FAA Approval and Travel-Friendly Features**
If you travel frequently, especially by air, be sure to select an FAA-approved portable oxygen concentrator. Features like compact size and easy battery swapping can make travel much more convenient【19†source】.
#### 7. **Cost and Insurance Coverage**
The cost of an oxygen concentrator can vary widely depending on the features, brand, and type of device. Check if your insurance covers part of the cost, or explore government assistance programs designed to help cover the expense.
---
### **Conclusion**
Oxygen concentrators have transformed the lives of many individuals suffering from chronic respiratory conditions. While they offer numerous benefits such as improved mobility, reduced costs, and customizable oxygen delivery, they also come with limitations, including initial cost, noise, and power dependency. By understanding the pros and cons of these devices and selecting the right model based on your specific



Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.